Searching for the right hearing aid involves more than just selecting a device; it’s about choosing a solution tailored to your unique hearing profile, lifestyle, and cosmetic preferences. Whether you’re managing mild or profound hearing loss, understanding the differences between device styles—and where to purchase them—can greatly impact your experience.
Choosing a professionally fitted hearing aid from an audiology clinic allows for full customization and expert support. On the other hand, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids offer accessibility but with fewer adjustments and more variability in comfort and effectiveness.
Types of Hearing Aids: ITE vs. BTE

There are two main categories of hearing aids, each available in multiple styles. These are:
- In-the-Ear (ITE) – Custom-fitted to sit inside the ear canal or bowl
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE), including Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) – Rest behind the ear with a receiver in the canal
| Feature | ITE | BTE/RIC |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Discreet or invisible in smaller models | More visible, but increasingly sleeker designs |
| Comfort | Good fit if custom molded; possible occlusion | Generally comfortable; more airflow, less occlusion |
| Sound Quality | Varies by model; sensitive to internal echo | Enhanced directional microphones |
| Wireless Features | Limited in smaller models | Typically Bluetooth-enabled with smartphone and TV streaming |
| Battery Life | Shorter; limited rechargeability | Longer; most models offer rechargeable options |
| Durability | More prone to earwax and moisture | Better protection; receiver is replaceable |
| Hearing Loss Range | Mild to severe | Mild to profound |
| Market Share | ~15% | ~85% |
| Price | Similar to BTE models | Similar to ITE models |
In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
ITE hearing aids are custom-molded to fit the ear canal or bowl and are favored for their discreet appearance. They’re often selected by those seeking invisible hearing aids or for users with dexterity challenges who benefit from larger controls such as rechargeable custom models.
These aids contain a microphone, amplifier, and speaker. They can range from completely-in-canal (CIC) models to full-shell versions that fill the concha for greater amplification.
ITE hearing aids are ideal for individuals with moderate dexterity and moderate hearing loss. However, they may not be suitable for individuals with good low-frequency hearing, as the occlusion effect can cause their voice to sound boomy or hollow.
When to Avoid ITE Hearing Aids
If you have significant low-frequency hearing or dislike how your voice sounds in enclosed devices, you might prefer RIC models. Always check for a return policy—especially when purchasing OTC invisible aids—to avoid being locked into an uncomfortable solution.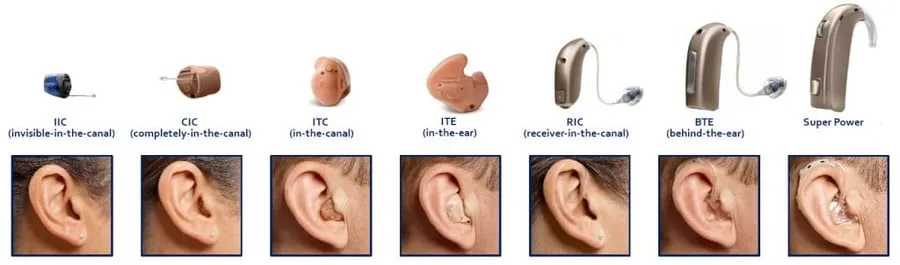
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) and Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) Hearing Aids
Today’s BTE hearing aids, especially Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) designs, have become the global standard for hearing care. Instead of housing all components in the ear, these devices sit comfortably behind the ear, transmitting sound into the canal via a thin wire with a small receiver (speaker) inside.
Because of their versatility, discreet styling, and superior sound processing, RIC hearing aids make up roughly 70–80% of all hearing aid fittings worldwide (per MarkeTrak studies).
Key Advantages of RIC Hearing Aids
Patients often choose RIC devices because they combine performance with comfort:
- Lightweight and comfortable – Slim design rests gently behind the ear.
- Discreet appearance – Nearly invisible when paired with skin-tone tubing.
- Natural sound quality – Receiver sits closer to the eardrum for clearer speech and high-frequency detail.
- Reduced feedback risk – Separation of microphone and receiver minimizes whistling.
- Flexible fittings – Use either soft silicone domes (open or closed) or custom earmolds.
- Excellent in background noise – Equipped with advanced directional microphones and noise reduction algorithms.
- Rechargeable options – Most models now include lithium-ion batteries for all-day power.
- Connectivity – Seamless streaming with smartphones, TVs, and Bluetooth accessories.
👉 For more detail on technology upgrades, see Best Hearing Aid for Background Noise.
Why Some Still Prefer ITE Hearing Aids
While RICs dominate the market, ITE hearing aids remain popular for certain users:
- Dexterity concerns – Larger ITE models are easier to insert and adjust, especially for patients with arthritis or tremors.
- Cosmetic preference – Invisible-in-canal (IIC) devices appeal to those who want nothing visible behind the ear.
- Physical limitations – Patients who wear glasses, oxygen tubing, or face masks may feel crowded behind the ear.
As an audiologist, I often recommend ITEs when hand strength and coordination are more important than advanced connectivity or background noise performance.
Which Style Is Right for You?
Ultimately, the “best” hearing aid depends on a balance of hearing needs, comfort, dexterity, and lifestyle. For example:
- If you’re socially active, frequently in noisy restaurants, or rely on smartphone streaming → RIC/BTE models usually perform best.
- If you prioritize invisibility and don’t need advanced wireless features → ITE models may be more appealing.
- If you have complex loss (like profound or mixed hearing loss) → only BTE models with custom earmolds may provide enough power.
Pro Tip: No matter which style you choose, ask about:
- Trial periods and return policies
- Real-ear verification testing (REM)
- Follow-up appointments for adjustments
These steps ensure you aren’t just buying a device—you’re investing in long-term hearing health.
Learn More: Your Complete Guide to Hearing Aids
Choosing between ITE and BTE/RIC hearing aids is just one part of the journey. To get the most out of your decision, it helps to understand the full picture—how hearing aids work, what features matter, and how to care for them over time.
That’s why I created a comprehensive hub page:
👉 Everything to Know About Hearing Aids
This resource brings together expert insights on:
- How hearing aids improve communication and brain health
- The pros and cons of different styles and brands
- Tips for daily wear, comfort, and troubleshooting
- Cost comparisons and insurance considerations
- Advanced technology like Bluetooth, telecoils, and Auracast
Whether you’re a first-time user or upgrading after years of experience, this guide will help you make a confident, informed decision.

