Updated for 2025: As an audiologist, I’m often asked about the differences between traditional hearing aids and the newer over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids. With the FDA’s recent introduction of OTC devices, many people—especially seniors—are wondering: How do they compare in performance, features, and total cost? In this guide, I’ll break down the pros, cons, and true costs of OTC hearing aids vs. professionally fitted traditional hearing aids so you can make the most informed decision possible.
OTC Hearing Aids vs. Traditional Hearing Aids: At a Glance
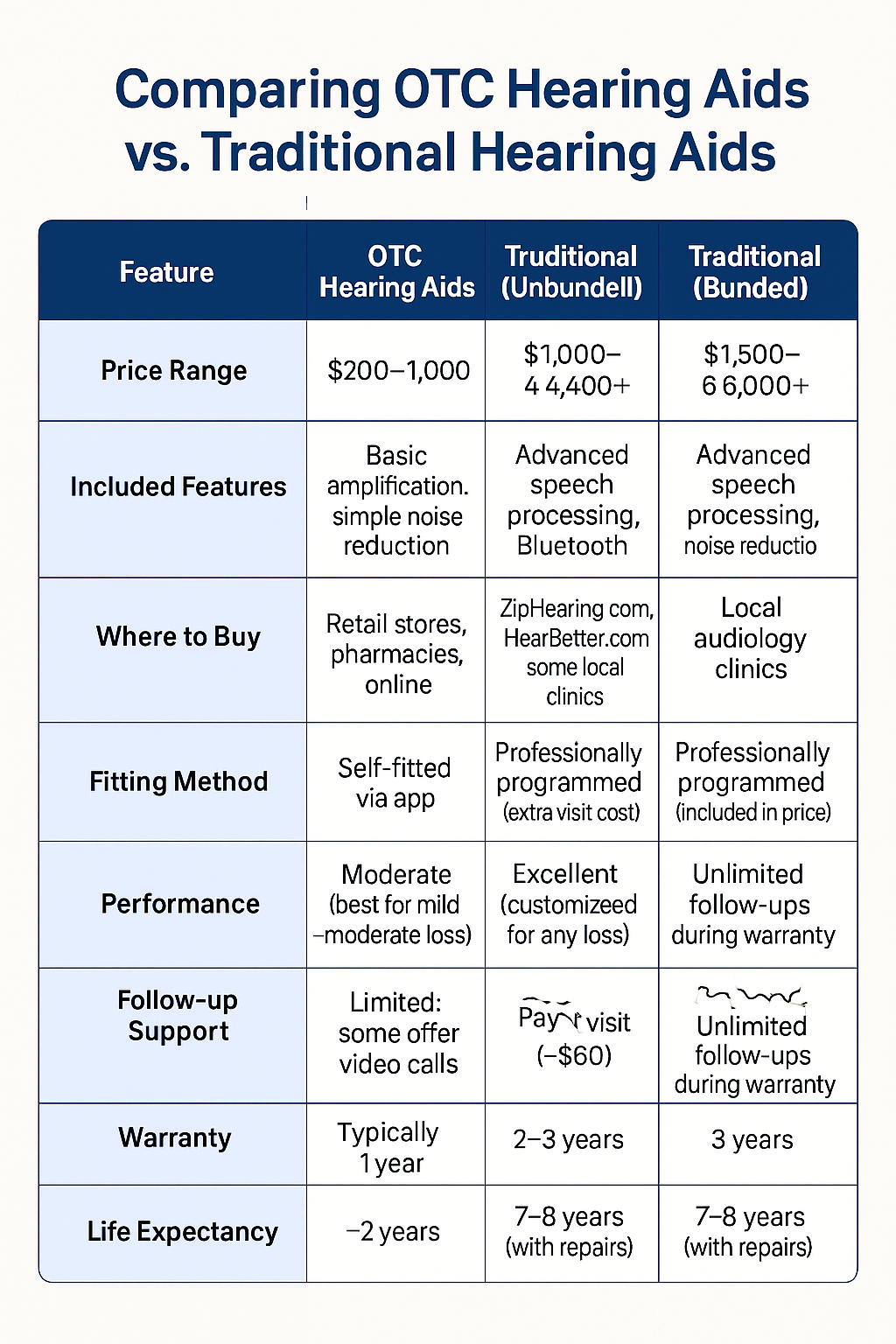
| Feature | OTC Hearing Aids | Traditional (Unbundled) | Traditional (Bundled) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Range | $200 – $1,000 | $1,000 – $4,400+ | $1,500 – $6,000+ |
| Included Features | Basic amplification, simple noise reduction | Advanced speech processing, Bluetooth, noise reduction | Advanced speech processing, Bluetooth, noise reduction |
| Where to Buy | Retail stores, pharmacies, online | ZipHearing.com, HearBetter.com, some local clinics | Local audiology clinics |
| Fitting Method | Self-fitted via app | Professionally programmed (extra visit cost) | Professionally programmed (included in price) |
| Performance | Moderate (best for mild–moderate loss) | Excellent (customized for any loss) | Excellent (customized for any loss) |
| Follow-up Support | Limited; some offer video calls | Pay per visit (~$60) | Unlimited follow-ups during warranty |
| Warranty | Typically 1 year | 2–3 years | 3 years |
| Repairs After Warranty | Not usually available; must replace device | ~$300, includes 6-month warranty | ~$300, includes 6-month warranty |
| Loss & Damage Policy | None; must buy new device | $350 deductible for replacement | $200 deductible for replacement |
| Supplies | ~$40/year | ~$40/year | ~$40/year |
| Life Expectancy | ~2 years | 7–8 years (with repairs) | 7–8 years (with repairs) |
What Are OTC Hearing Aids?
OTC hearing aids are FDA-approved devices sold without a prescription, intended for adults with mild to moderate hearing loss. They’re self-programmed using an app and offer basic controls like volume and preset sound settings. Available in behind-the-ear (BTE) and in-the-ear (ITE) designs, they’re mass-produced for affordability—but they’re not custom molded, and fine-tuning is limited compared to professional fittings.
What Are Traditional Hearing Aids?
Traditional hearing aids are prescribed and programmed by a licensed audiologist after a comprehensive hearing test. They come in multiple styles—RIC/BTE, invisible-in-canal, and custom earmold designs—and include advanced technology like directional microphones, Bluetooth streaming, wind noise management, telecoils, and adaptive background noise reduction.
Key Factors Affecting Cost
- Manufacturing Process: Custom molds and individualized programming add cost but improve fit, comfort, and performance.
- Distribution Channel: Buying through a clinic includes service; online OTC sales reduce overhead, lowering price.
- Regulatory Compliance: Traditional devices meet stricter FDA standards, while OTC devices meet lower compliance levels.
- Insurance Coverage: Some private plans help cover traditional aids; OTC devices are almost never covered.
- R&D Investment: Major brands like Phonak and ReSound spend millions improving tech; OTC brands often use older designs.
Audiologist’s Advice
If you have straightforward, mild hearing loss and want an entry-level, budget-friendly option, OTC aids may work well—especially if you’re comfortable with smartphone apps. If you have moderate to severe hearing loss, tinnitus, or complex listening needs, professionally fitted hearing aids are worth the investment. Most importantly, don’t leave hearing loss untreated; even mild loss can impact relationships, work performance, and cognitive health.
When comparing the price tag of OTC hearing aids to traditional, professionally fitted devices, the difference can feel overwhelming. But cost alone shouldn’t determine your decision—support, customization, and long-term results all matter. To better understand how pricing connects with performance, check out our complete OTC hearing aid guide.