By Jonathan Javid, Au.D. — Clinical Audiologist (14+ years; 10,000+ patient visits)
Disclosure: This guide may contain referral links that help support HearingInsider.com at no additional cost to you.
Average Cost of Hearing Aids in 2025
Across U.S. clinics, a single prescription device commonly ranges $2,000–$3,500, or $4,000–$7,000 per pair. Over-the-counter (OTC) devices usually range $200–$1,500 per device, best suited for adults with mild hearing loss.
For a deeper dive into specific price bands and cost variables, see my supporting article: How Much Do Hearing Aids Cost?
Price Comparison by Purchase Source
Where you buy affects both the price and the level of service you receive:
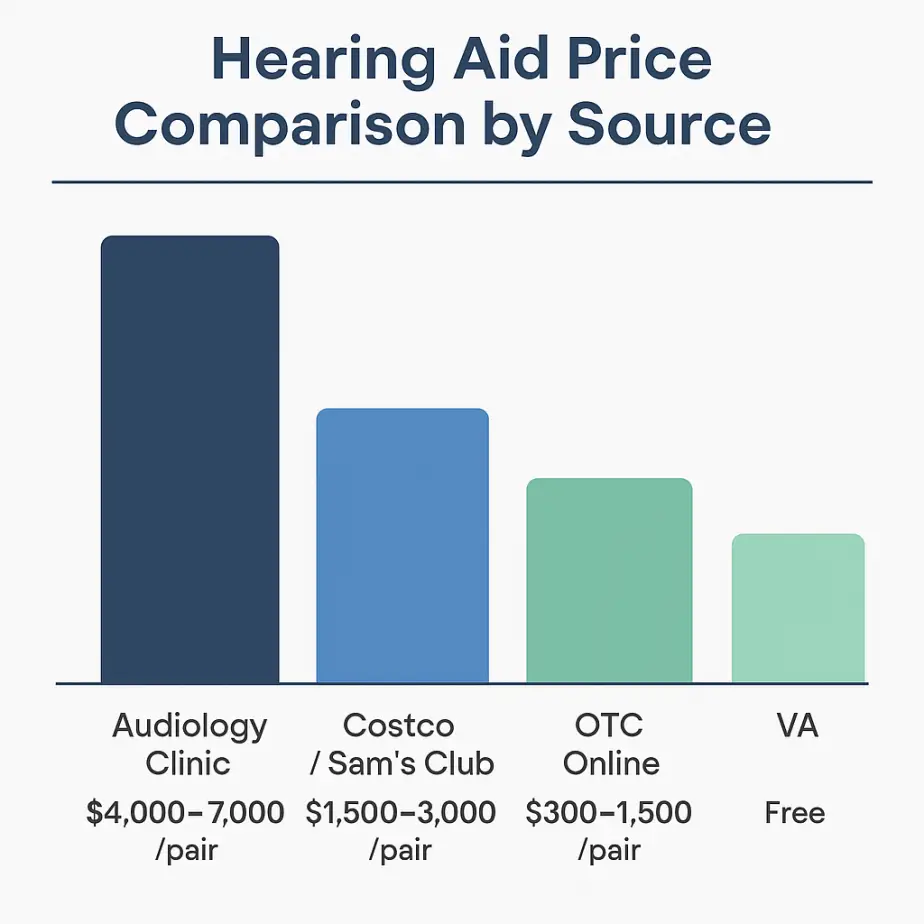
| Source | Typical Price (Pair) | Services Included | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audiology Clinic | $4,000–$7,000 | Diagnostic testing, custom fitting, follow-ups, warranty | Personalized programming & complex listening needs |
| Costco / Sam’s Club | $1,500–$3,000 | Basic fitting, limited brands | Value shoppers wanting good tech at lower cost |
| OTC Online | $300–$1,500 | Device only or virtual support | Adults with mild loss & high tech comfort |
| Veterans Affairs (VA) | Free (qualifying veterans) | Full services and repairs | Eligible veterans—always check VA first |
Why Hearing Aids Are So Expensive
Three main drivers explain the price:
- Technology R&D: Ultra-mini chips, multi-mic beamforming, and AI noise reduction require years of investment.
- Professional Services: Clinical testing, real-ear measurements, counseling, and follow-up adjustments are often bundled into device price.
- Insurance Gaps: Many plans provide little or no direct device coverage, shifting cost to the consumer.

Explore the service and maintenance side in my hub: Complete Guide to Hearing Aid Maintenance & Repairs.
OTC vs. Prescription Hearing Aids
OTC hearing aids (authorized for adults with mild–moderate loss) can be a cost-effective entry point. Prescription devices provide custom programming, more advanced features, and a clinical relationship that many patients need.
- Start with: Everything to Know About Hearing Aids
- If restaurant noise is your priority: Best Hearing Aid for Background Noise
What Is Usually Included in the Price?
- Diagnostic hearing evaluation and needs assessment
- Custom fitting + real-ear verification
- Follow-up fine-tuning visits
- Manufacturer warranty (often 2–3 years) + loss/damage coverage
Unbundled models (some warehouse clubs and online sellers) may charge separately for testing and follow-ups.
Costs by Style
- CIC / ITE (custom in-ear): $1,500–$3,500 per device
- RIC / BTE (receiver-in-canal / behind-the-ear): $2,000–$3,800 per device
- Premium RIC (rechargeable + Bluetooth): $3,000–$3,800 per device
Compare styles here: ITE vs BTE Hearing Aids
When Paying More Makes Sense
- You struggle in noise and need advanced processing
- You value seamless Bluetooth calls/music
- You want rechargeable convenience
- You need tinnitus features or special programs
Otherwise, a mid-level model often delivers 80–90% of the benefit for much less.
How to Save on Hearing Aids
- Ask clinics about unbundled pricing for transparency.
- Compare with warehouse clubs if you don’t need wide brand choice.
- Consider OTC for mild loss and good app skills.
- Protect your hearing to delay upgrades: Custom Earplugs
- For swimmers or beachgoers, see: Best Waterproof Hearing Aids
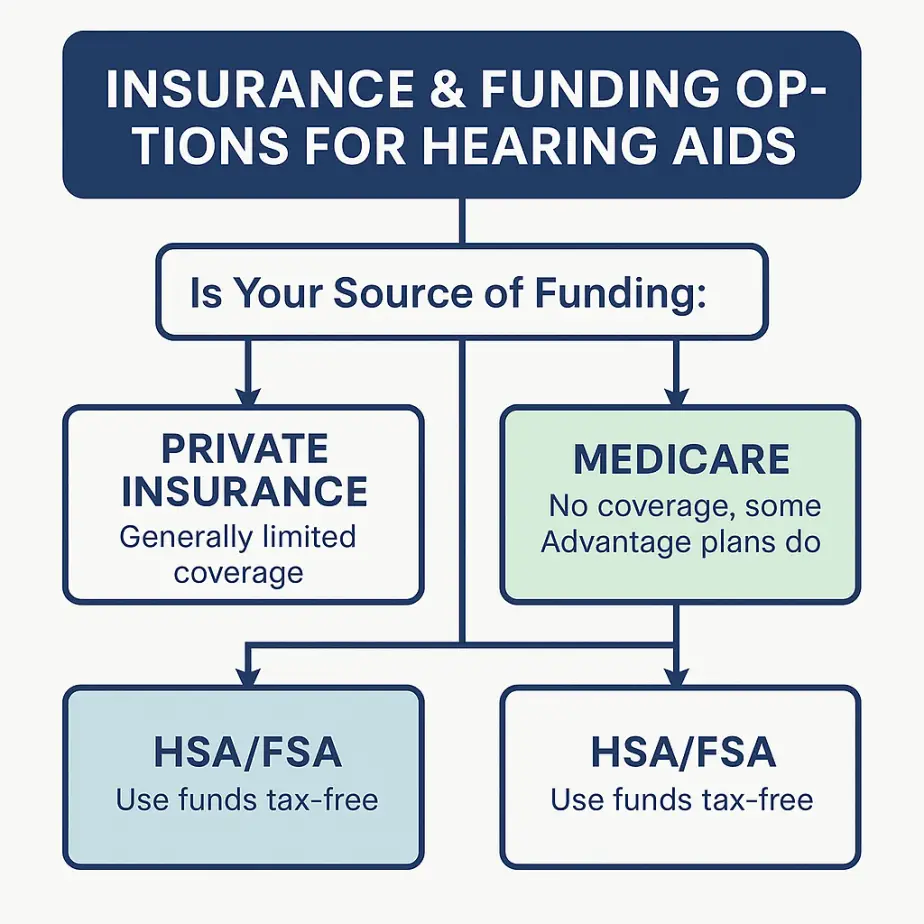
Insurance & Funding Options
- Private Insurance: often limited benefits or allowances.
- Medicare: traditional Medicare doesn’t cover devices; some Advantage plans include partial benefits.
- VA Benefits: qualifying veterans receive hearing aids and services at no cost.
- HSA/FSA: pay with pre-tax funds — Using HSA & FSA Funds for Hearing Aids.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why aren’t hearing aids covered like eyeglasses?
Coverage varies by plan and state. Many insurers categorize hearing aids differently from vision services and provide limited allowances.
What’s the cheapest way to get hearing aids?
OTC or warehouse clubs typically have the lowest sticker price. However, factor in support—some patients benefit from clinic-level customization that reduces returns and re-purchases.
Are OTC hearing aids worth it?
Yes for mild losses and motivated tech users. Anyone with moderate–severe loss, difficulty in noise, or medical concerns should consider prescription devices.
How long do hearing aids last?
Most users replace devices every 5–7 years due to wear, battery life, connectivity standards, and improvements in speech-in-noise performance.
Do clinics match Costco’s prices?
Not usually. Clinics bundle more comprehensive testing, verification, and follow-up care, which justifies the higher total price.

