Written by an audiologist with thousands of patient visits. Practical, empathetic, and actionable.
Why Your Ears Ring After a Concert (and Why It Matters)
If you’ve ever walked out of a concert or game with your ears ringing and the world sounding “muffled,” your ears were telling you: that was too loud for too long. For most people, that ringing fades. For some, it never stops.
“If I had only known, I would’ve worn earplugs.” — a sentence I wish I heard less often in clinic.
This guide explains what’s happening inside the ear, the warning signs to watch for, and exactly how to protect your hearing—without giving up the things you love.
What Is Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) happens when loud sound damages the delicate hair cells in the inner ear. Unlike a cut on your skin, these cells do not regenerate. That’s why prevention is everything.
The World Health Organization estimates over 1 billion young people are at risk from unsafe listening. In the U.S., the CDC reports roughly 12% of adults already have measurable noise damage.
How Loud Is Too Loud?
Think of sound like sun exposure: the louder it is, the less time you can safely spend in it.
| Sound Source | Decibels (dB) | Safe Exposure* |
|---|---|---|
| Busy Traffic | 85 | ~8 hours |
| Lawn Mower | 90 | ~2 hours |
| Rock Concert | 110 | < 5 minutes |
| Gunshot | 150+ | Instant damage |
*Based on NIOSH guidance. Dive deeper in How Loud Is Too Loud? Understanding Safe Decibel Levels.
Everyday Causes (It’s Not Just Concerts)
- Headphones & Earbuds: If you routinely go past ~60% volume, risk climbs fast. See Safe Listening With Headphones.
- Concerts, Clubs & Stadiums: Often >100 dB. Earplugs keep the fun, lower the harm. For families: Hearing Protection for Kids.
- Workplace Noise: Construction, manufacturing, aviation, agriculture. Know your rights: OSHA standards explained.
- Motorcycles & Powersports: Helmet wind can exceed 95 dB. Options in Hearing Protection for Motorcyclists.
- Firearms: One unprotected shot can cause permanent damage. Best Hearing Protection for Hunters & Shooters.
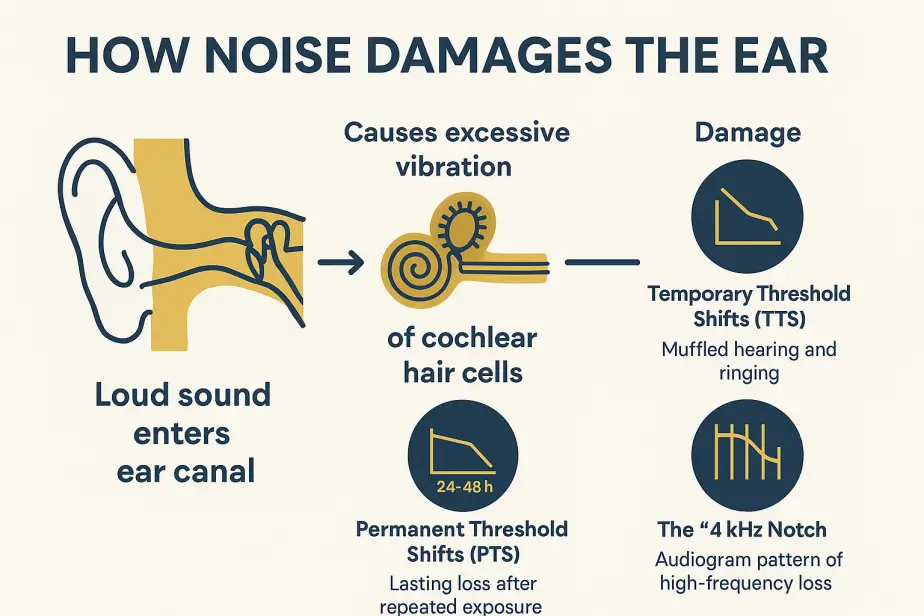
What Noise Does Inside the Ear
Inside the cochlea, rows of hair cells convert vibration into electrical signals. Loud sound bends these cells too far, too fast. Short-term damage causes Temporary Threshold Shifts (TTS)—muffled sound and ringing that may fade in 24–48 hours. Repeated TTS leads to Permanent Threshold Shifts (PTS). On an audiogram, NIHL often shows a classic 4 kHz notch.
Symptoms to Take Seriously
- Tinnitus (ringing, buzzing, hissing) after noise exposure
- Muffled hearing or “cotton in the ears” sensation
- Struggling to follow speech in restaurants or noisy rooms
- Needing the TV/phone louder than others prefer
If this sounds familiar, act now. Start here: Tinnitus After Loud Events: What to Do Immediately.
Prevention That Actually Works
Protection Options (Quick Comparison)
| Type | NRR | Best For | Why Choose It | Tradeoffs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam Earplugs | 20–33 dB | Concerts, sleep | Cheap, widely available, very effective if inserted properly | Fit can be tricky; can muffle music |
| Musician’s Earplugs | 10–25 dB | Performers, music lovers | Even attenuation keeps sound quality natural | More expensive than foam |
| Custom Earplugs | Up to ~30 dB | Frequent users | Perfect fit, comfortable for hours | Requires audiologist visit |
| Earmuffs | 20–30 dB | Worksites, yard work | Consistent fit, easy on/off | Bulky, warm |
| Electronic Shooters’ Muffs | Up to ~30 dB | Ranges, hunting | Amplify voices/environment, block blasts | Battery-powered, pricier |
Listening Habits That Lower Risk
- Follow the 60/60 rule: max 60% volume, 60 minutes at a time.
- Use noise-cancelling headphones to avoid cranking the volume.
- Take “quiet breaks” so ears can recover.
- Use a free decibel meter app to audit your daily sound exposure.
Workplace Hearing Conservation: OSHA vs. NIOSH
| Standard | Limit | Approx. Safe Time |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA | 90 dB | 8 hours |
| NIOSH | 85 dB | 8 hours |
| NIOSH | 100 dB | 15 minutes |
Learn what employers must provide in Why Some Jobs Require Mandatory Hearing Tests.
Treatment & Management (There’s Real Help)
- Hearing Aids: Enhance speech clarity, reduce background noise, and stream calls/media.
- Tinnitus Therapy: Sound therapy, counseling, and hearing aids with tinnitus features can help.
- Cochlear Implants: For severe loss when hearing aids aren’t enough.
- Communication Strategies: Face the talker, reduce background noise, and consider assistive mics.
FAQs
- Can noise damage be reversed?
- No. But you can prevent additional loss with protection and safer habits.
- Are kids more vulnerable?
- Yes—early damage affects a lifetime of learning and communication. See protection for kids.
- Do hearing aids cure NIHL?
- No, but they often dramatically improve speech understanding and quality of life.
- Are AirPods safe?
- They can be—keep volume modest and take listening breaks. Noise-cancelling can help you listen at lower levels:
Do Noise-Cancelling Headphones Protect Hearing? - How do I insert foam earplugs correctly?
- Roll tightly, pull your ear up/back, insert deeply, then hold for 20–30 seconds while it expands.
Next Step: Understand Your Hearing Baseline
A professional audiogram provides a reference point and helps catch noise damage early. Ask your local clinic or workplace program about scheduling options.
- Objective results across frequencies (watch for the classic 4 kHz notch).
- Personalized prevention plan + hearing protection recommendations.
- Optional tinnitus counseling.

